The Payments Business
Klarna has sold its gateway business to a local investor consortium for $520m. Klarna Checkout (KCO) claims 40% share of its home market of Sweden and 20% across the Nordics as a whole.
It’s obvious why Klarna is selling. KCO competed with key distribution partners such as Stripe and Adyen and the very generous sale proceeds will bolster Klarna’s balance sheet and help grow its lending business.
But it’s less clear how KCO’s new owners will make a return on their investment. Stand-alone gateways have been under considerable pricing pressure in recent years, and many have ended up vertically integrated into the larger merchant acquirers.
In banking news, BNP Paribas and BPCE, which together handle c.30% of card payments in France, will invest €100m each and pool their payment capabilities to create a joint-venture with the scale to compete with Worldline and Nexi. Technology will be “home grown” and most likely a continuation of Partecis, an in-house platform based on ACI products. While there’s plenty of scope for synergy in France, the JV will find its hoped for international expansion rather more challenging as PagoNxt, Santander’s payment unit, demonstrated when it recently closed its German operations.
As predicted in last month’s Business of Payments, Sabadell has postponed the sale of its merchant services business to Nexi. Sabadell is subject to a hostile takeover from BBVA, another Spanish bank. BBVA has a good in-house payment offer and has less need of Nexi’s products.
IDC, a London-based research firm, has published vendor evaluations for online and omni-channel retail payments. The full reports cost $20,000 each but the top ranked firms have helpfully made their sections available free of charge. Stripe comes top for online payments although is marked down for being expensive. Adyen is first for omni-channel but customers are warned that its all-in-one solution may lack flexibility.

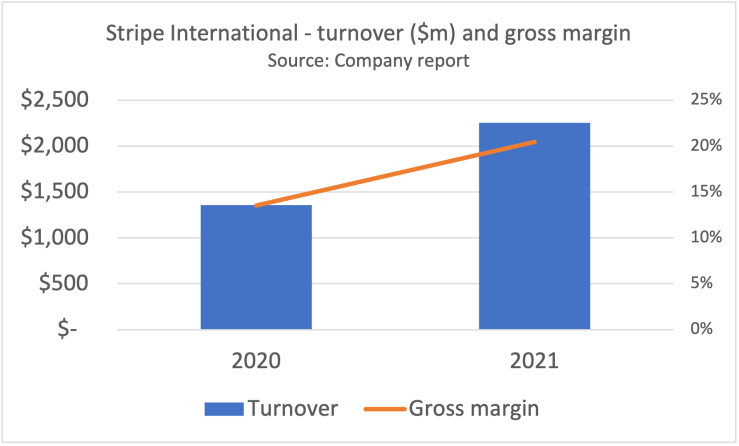
Stripe is notably missing from IDC’s omni-channel evaluation but is quickly becoming a very credible option for cross-channel merchants in Europe. Stripe has launched a suite of new enterprise services in France including its S700 POS terminal, acceptance of Carte Bancaire and an integration with CEGID, a leading local retail ISV. Stripe claims half the CAC-40 companies as customers and announced that Accor, the hotel group with over 5,600 locations worldwide, is standardising on Stripe for its new, centralised booking system. Stripe obsessives will enjoy this detailed history of the business.
Viva Wallet’s lawsuit with JP Morgan ended in a London courtroom with both sides claiming victory. JPM paid an eye-popping $800m for 48.5% of Viva in 2022, primarily to gain access to SME customer onboarding tools for European markets. Haris Karonis, Viva’s founder, claimed that JPM then deliberately blocked his company’s launch in the US so that the giant American bank could buy the rest of Viva on the cheap. JPM counter-claimed that Karonis failed to understand how far Fintech valuations had fallen.
Financial results of listed payment companies have settled down post-pandemic into a phase of steady but unspectacular growth. FXC have crunched the Q1 numbers so you don’t have to.

A wero for your thoughts

It’s taken four years and 14 of the original 31 banks have exited the consortium but the European Payment Initiative (EPI) has finally launched wero, the long-long-awaited domestic European payment champion. Wero, a combination of “we” and “euro”, is live for person-to-person money transfer, initially for customers of co-operative and savings banks in Germany and KBC in Belgium. French banks come on stream in the autumn.
Shoppers will be able to make eCommerce payments with wero from early 2025 and Computop, the German PSP, has already begun asking merchants to register to be part of a pilot. In-store payments will follow in 2026.
Payments & Banking, a German blog, explains what wero is and what it is not.
The consensus from payment experts is that for wero to succeed the EPI needs to focus ruthlessly on user experience and keep the member banks firmly in the background. And “I need a wero” is the only song that will do as you can hear in this short commercial.
Paydirekt and Sofort axed
Even though wero is at least six months away from being ready for eCommerce, its launch sparked the unexpectedly early closure of Paydirekt/Giropay, a domestic competitor to PayPal launched by the German banks in 2016.
Insiders tell me that the service termination was badly handled. Giropay switched off its old integration interface at the end of June even though many acquirers had not yet migrated to the new version.
Meanwhile, Klarna has announced the closure of Sofort, the German online bank transfer service which it bought for $150m in 2013. Merchants will be migrated to Pay Now, Klarna’s open banking product. This includes buyer protection which is great for shoppers but less exciting for Sofort’s many merchants in the gambling and adult sectors. These customers will be looking for alternatives.
Klarna’s new wrapper doesn’t come cheap. In Germany, Adyen is charging 1.35% + €0.20 for Klarna Pay Now transactions. For UK merchants, Mollie is asking a punchy 4.99% + £0.30.
If that wasn’t enough disruption, Shopify is deactivating Amazon Pay as a payment option from all European merchants. No reason was given and merchants are really unhappy.
Scheming
Blik, the wildly successful Polish mobile payment standard, continues its stunning growth with payment volume up 53% in 2023 to €29bn. Blik is jointly owned by Mastercard and a number of local banks who have suddenly woken up to the importance of their investment. From now on, the banks will send their CEO’s to Blik’s board meetings.

Bancomat, the Italian domestic debit scheme, is finally getting its act together. Milan-based investment fund FIS has made a €100m investment, the board has been slimmed down to speed decision making and a new CEO appointed from Mastercard. Nexi runs the technology for Bancomat and has put the card scheme live on Apple Pay and as a payment option on Amazon.
Read more about Bancomat’s 2023 results on the Business of Payments blog.
ISV
We’re taking a keen interest in the convergence of software and payments. Flagship Consulting’s latest report shows quite how dependent many American ISV’s have become on payment and other financial services revenue.

In response, payment processors know they need to partner with ISVs and some have gone further, buying or building an in-house range of vertical software.
Intriguingly, the stock market value of payment processors that offer software is rather lower than software vendors that offer payments processing. Jevgenijs Kazanins looks at why Toast (an ISV that offers payments) is valued more highly than Shift4 (a processor that offers software) even though Toast makes much less money. His conclusion is that ISV’s are better at securing recurring revenues under contract.
European ISV’s have now realised they too can make money from processing. The opportunity is smaller than in North America because payment margins in Europe are much lower. Nevertheless, a savvy commerce software vendor can still double profit margins by embedding payments in its core merchant offer.
With so many acquirers and PSP’s pivoting towards ISV’s as their primary distribution channel, a number of start-ups have begun offering key parts of the technology stack as-a-service. Here are a few that have caught my eye.
- Chift, based in Brussels, offers PSPs connections to a range of leading accounting, eCommerce and ePOS software though a single API. The company just raised €2.3m
- Shape Technologies is offering payments-platform-as-a-service to payment facilitators with capabilities including onboarding, KYC and billing. Shape is founded by alumni from Cardstream and is helping put Taunton, Somerset on the Fintech map.
- Fung, in Amsterdam, offers a similar product set to Shape but is also a payment institution and can handle the money flow too.
- Dublin/Vilnius based Paynt, goes one step further with a full acquiring-as-a-service proposition.Subscribe
New shopping
We’re keeping a close eye on the progress of autonomous stores as one possible driver of a seismic shift in grocery transactions from POS to the shopper’s phone.
Rewe is leading the deployment of “just walk out” formats in Europe. The German supermarket giant has opened a 1200 sq metre autonomous store in Hamburg using technology from Trigo which can even identify fresh meat and cheeses picked from the deli counter. Showing confidence in the concept, even where labour costs are much lower than Germany, Rewe has also opened an autonomous store in Bucharest.
Although sceptics point out that frictionless checkout often involves more manual intervention than the vendors let on, the use cases are multiplying. For example, in a village store in Switzerland a shipping container is transformed into an unmanned convenience store (or walk-in vending machine) using technology from FastaXs.
Biometric payments
With early pilots looking positive, there’s growing momentum behind new biometric payment technology in the US, including palm payments (favoured by Amazon) and even face payments. JP Morgan is taking an interest in the latter with a partnership with PopID, a Californian start-up which has an early lead in the technology.
In Europe, Mastercard is backing PayEye, a Polish start-up which is piloting its iris/facial recognition product at five locations of Empik, a large retailer of books, toys and games.
Digital reciepts
A number of start-ups are trying to make it easier for merchants and consumers to move to digital receipts. Habits are hard to shift. Despite a new legal requirement in France that paper receipts should be opt-in only, Auchan, the grocery chain, reports 60% of shoppers still ask for paper.
- In the UK, Slipp, which boasts JD Sports as an early client has raised £750K. Slipp integrates with the ePOS software to send the shopper a text or email. JD Sports says using Slipp’s SMS receipts to promote its loyalty programme is increasing the number of customer sign-ups.
- Anybill, from Regensberg in Germany, asks customers to scan a QR code presented by the ePOS. Pricing ranges from €4.49 to €35.99 per month per outlet.
- Yocuda, a French start-up acquired by Global Blue, claims to have delivered over 2m electronic receipts to over 200,000 identified shoppers. Clients include Halfords and Decathlon.
- Receipt Hero, based in Helsinki, has raised additional funds to supplement the $5.7m already invested. Receipt Hero offers cardlinking as well as QR scans. Partners include PayOne.
- Pi-xcels from Singapore has an elegantly simple product that delivers an e-receipt automatically when the shopper taps their phone on the payment terminal. The product integrates with the terminal not the ePOS software and is available on Ingenico and PAX.
There’s an open question whether digital receipts can establish themselves as product category in their own right or whether merchants would prefer to buy the capability as a feature of existing POS or CRM software.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is moving up and down the hype curve faster than any previous technology as Benedict Evans explains. McDonalds has already hit the trough of disillusionment and shut down a pilot with IBM that used AI to automate order taking at 100 drive-thru restaurants. The robots made too many mistakes such as adding bacon to ice cream.
Worldline is taking a more measured pace and has detailed how it is managing its AI initiatives. This is 1500 words of big company governance, stage gates and committees. I wish them luck.
SoftPOS
This technology, which allows any off the shelf consumer device to accept contactless card payments, was originally touted as a micro-merchant proposition but is proving most popular with large enterprises.
LVMH is leading the innovation. Liberated from the need to locate the nearest payment terminal, sales associates at Christian Dior, an LVHM brand, each have their own iPhone to serve customers wherever they are in the store. Dior has worked with Adyen, Global Blue and Vo2 Group, a Paris HQ’d tech consultancy, to add instant VAT tax refunds to the proposition.
In vendor news, Rubean, based in Munich, has raised an additional €2m capital to finance its strong growth. Sales are forecast to rise to €2.2-€2.5m this year from €1m in 2023 on the back of new distribution deals.
Rubean’s partnership with Global Payments may be threatened by the Atlanta processor’s unpublicised purchase of Yazara. The Global/Yazara tie up is likely also to be bad news for MyPinPad which local sources suggest may be replaced as supplier to eService, Poland’s largest acquirer, which Global bought last year.
In better news for MyPinPad, Ur&Penn, a leading chain of jewellers in Norway, is using its SoftPOS application to take store payments on the associate’s Android phones. 2izii is the integrator and Elavon the acquirer.
Phos, acquired by Ingenico in 2023, is making good progress building out its distribution network, announcing a key partnership with Shift4, a US processor with big ambitions in Europe. Phos is also the technology partner for BORICA, which provides SoftPOS to the three largest banks in Bulgaria. BORICA claims 1,500 “terminals” live today.
In Italy, Ultroneo has implemented MarketPay’s PayWish SoftPOS application for its Get Your Cash merchant proposition. Volumes are growing swiftly (see below) but it’s not been plain sailing. Writing on LinkedIn, one Ultroneo director explained “For nearly 12 months now we have been struggling with the teething problems of this new technology. Bug after bug, incident after incident, we have managed to stabilize the SoftPos to the delight of our customers.”

Openbanking
The UK’s incoming Labour government is making very positive noises about fintech. Quoting from its manifesto: “Financial services are one of Britain’s greatest success stories. Labour will create the conditions to support innovation and growth in the sector, through supporting new technology, including Open Banking and Open Finance and ensuring a pro-innovation regulatory framework.”
There is much that a new regulatory approach could deliver, including an open banking acceptance mark, “scheme” rules to ensure common standards for authorisation codes, refunds etc, the introduction of consumer protection and a recognition that all this cannot be provided free of charge.
Positively, the number of open banking payments made in the UK rose c.50% year-on-year to 17m in May 2024. Variable Recurring Payments (VRPs), the open banking equivalent of direct debits, now account for 11% of the total.
The increase is encouraging but compared with the 2bn debit card transactions made in the UK in a typical month, volumes remain very small.

The slow take up of open banking has implications for the large number of vendors operating in this sector. There are twenty listed on the UK government’s procurement framework alone. If revenues don’t arrive soon, only the best capitalised will be able to keep trading until the product goes mainstream.
Truelayer, hopes to be one of the survivors, having raised a remarkable total of $271m from its investors. Truelayer’s CEO has given an interview to explain that he is playing a long game, saying “We are an infrastructure business. That means we are likely going to spend a lot of time and a lot of years building and spending money before actually earning,”Subscribe
Cash
Germany is often cited as the last hold-out of the cash economy but the latest Bundesbank payment survey shows a further decline in the use of paper money. The cash share of transactions fell 7% points in 2023 to 51% and its share of volume by 4% points to 26%.
Old habits die hard. A Bavarian bar-owner called the police after a Latvian customer paid for 16 beers with 16 separate card transactions.

It’s no surprise that policy-makers in many countries are grappling with the implications of the world going cashless. For example, Ireland has passed an “Access to Cash” law which gives the government powers to set minimum numbers of ATMs for each area. The local banks, and their customers, will bear the cost. Revolut, wildly popular in Ireland, will likely get a free ride.
Without this kind of subsidy, independent operators will stuggle. In Poland, Euronet, which manages 50.000 ATMs, limited withdrawals to PLN200 (€46) for one day as a protest at the government’s refusal to let it to charge for transactions. Euronet complains that it is losing money because local banks pay just PLN 1.2 (€0.28) per withdrawal. We assume that Euronet probably more than makes up for the shortfall with its eyewatering DCC charges for tourists.
An enterprising British artist commented on his struggles to find a place to withdraw cash by fixing an ATM to a bridge in the middle of a river.

Of course, even if cash is available, retailers may decide not to accept it. This British pub says it has saved 12 hours work each week by going cashless. Cash is expensive to handle and the costs grow as volume declines. The Portuguese Central Bank believes cash costs merchants 2.96% compared to 0.78% for debit cards.

Crypto corner
Crypto currencies are assets not money, yet vendors persist in bringing forward payment acceptance solutions at POS.
“Few have heard of SpacePay, but give it a year, and it will likely be a household name” is the bold claim from this London based start-up which graduated from Barclays’ fintech accelerator. SpacePay, which has raised $750K, says it will allow people to spend crypto at “most existing point of sale card machines.” It’s not clear how this would work in practice.
If there is a user base for crypto at POS anywhere, it’s going to be in a cross-border market such as Luxembourg where some shoppers may not want their home country authorities to know what they are buying.
Done4You, an ISO based just across the border in Namur, Belgium, has implemented crypto at POS for a petrol station in the Grand Duchy using GoCrypto’s technology. Crypto transaction are 1.25% compared to interchange + 0.5% for credit cards.
In other news
Fiserv’s brand association with the Republican National Convention in Minneapolis is dividing opinion.
Good news for travellers. International cards are finally accepted at 97% of Dutch payment terminals and will reach 100% by the end of this year.
The Netherlands experienced its longest payment outage for five years as 30%-40% of PIN transactions failed over a three hour period. The problem was blamed on Equens (Worldline), the domestic inter-bank network. Worldline is also reportedly behind a shorter outage affecting UK grocers earlier this month.
A sign of the times. Such is the consumer uptake of Apple and Google Pay, one French bank has found that 20% of customers opt not to be sent a physical card.
Advent, whose portfolio companies include MangoPay, Planet and MyPOS, is excited about vertical payment/software bundles, specialist tools to support eCommerce and solving cross-border challenges.
Follow the money. European VCs have picked their top payment start-ups.
We’ve not seen many layoffs recently but Rapyd, the Israeli acquirer/processor, is cutting 30 posts in its home country.
TSG, an American consulting business, runs an annual payments API competition. Adyen is the overall winner with Square as runner up.
And Finally
Stripe has opened a new London office and is celebrating with a rather mystifyingbrand advertising campaign aimed at enterprise customers.

Photo credit Jevgenijs Kazanins
How to get in touch
Geoffrey Barraclough
geoff@barracloughandco.com